This document is relevant for: Inf1, Inf2, Trn1, Trn2, Trn3
AWS Neuron Dynamic Resource Allocation (DRA) Beta#
What is DRA?#
Prior to Kubernetes 1.33, Kubernetes used device plugins for resource management. The Neuron device plugin implements the device plugin interface to allow Kubernetes scheduler to manage Neuron resources. However, the device plugin framework only tracks device count—the scheduler cannot see device attributes. Due to this limitation, the framework cannot natively facilitate attribute-based filtering during device selection. For example, the default Kubernetes scheduler prior to DRA cannot support allocation of connected devices without additional mechanisms such as a scheduler extension.
Dynamic Resource Allocation (DRA) is a new framework for advanced resource management that addresses this limitation. DRA enables the scheduler to see the device attributes, allowing workloads to select devices based on specific attributes and achieve topology aware allocation. Hardware vendors determine which attributes are published for their hardware. The AWS Neuron DRA driver implements the kubelet plugin for DRA for AWS Trainium instances.
For more information on DRA, refer to Kubernetes Dynamic Resource Allocation.
Where can I get the Neuron DRA Beta driver and resource templates?#
To review and download the individual Neuron DRA Beta driver installation scripts, Kubernetes manifests, and resource claim templates, visit this page:
You can also download all of the Neuron DRA files and scripts from the link below:
Download the scripts and YAML files as a TAR/GZIP archive
Preserve the directory structure when you extract the archive. The driver installation script uses this relative folder structure to find the corresponding YAML files.
Directory structure:
containers/files/
├── manifests/
│ ├── clusterrole.yaml
│ ├── clusterrolebinding.yaml
│ ├── daemonset.yaml
│ ├── deviceclass.yaml
│ ├── namespace.yaml
│ └── serviceaccount.yaml
└── examples/
├── scripts/
│ └── install-dra-driver.sh
└── specs/
├── 1x4-connected-devices.yaml
├── 2-node-inference-us.yaml
├── 4-node-inference-us.yaml
├── all-devices.yaml
├── lnc-setting-trn2.yaml
└── specific-driver-version.yaml
What are the benefits of using DRA over device plugin?#
Reduced developer complexity
Device plugin-based workloads use node labels along with request and limits to allocate right resources. Example:
Worker:
replicas: 4
template:
spec:
containers:
- image: <aws-account-id>.dkr.ecr.us-west-2.amazonaws.com/neuronx_nemo:latest
name: mpitest
imagePullPolicy: Always
resources:
limits:
aws.amazon.com/neuron: "16"
vpc.amazonaws.com/efa: "16"
requests:
aws.amazon.com/neuron: "16"
vpc.amazonaws.com/efa: "16"
volumeMounts:
- name: dshm
mountPath: /dev/shm
volumes:
- name: dshm
emptyDir:
medium: Memory
DRA introduces ResourceClaim and ResourceClaimTemplates which provide abstraction:
Worker:
replicas: 4
template:
spec:
containers:
- image: <aws-account-id>.dkr.ecr.us-west-2.amazonaws.com/neuronx_nemo:latest
name: mpitest
imagePullPolicy: Always
resources:
claims:
- name: neurons
volumeMounts:
- name: dshm
mountPath: /dev/shm
volumes:
- name: dshm
emptyDir:
medium: Memory
resourceClaims:
- name: neurons
resourceClaimTemplateName: efa-neurons-4-devices
The ResourceClaimTemplate name is a given name and can be defined by the ML infra operators to be friendly to their developers. The RCT
definition translates the name into the underlying allocation details - these are abstracted away from ML developers.
Rich interface for resource requests
With DRA, resource requests can specify attribute-based selection. For example, RCT can follow requests, which was not possible to do with device plugins without additional node labeling and extensions. This interface allows us to facilitate topology-aware scheduling.
Allocate connected neuron devices from trn2 instance type and the devices in the set need to be running specified Neuron driver version.
Allocate a specific set of neuron devices for my pod - I want the pod to use devices in row 1 of the topology.
Dynamic configuration
DRA allows end users to specify additional configuration for the device via RCT. The Neuron DRA driver leverages this capability to allow ResourceClaimTemplates to specify LNC size to be used for the allocation. An example is shown below. The end user need not configure LNC via launch template while using Neuron devices with Neuron DRA driver.
#Template will be vended by Neuron via documentation/code repo
apiVersion: resource.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: ResourceClaimTemplate
metadata:
namespace: neuron-test7
name: lnc-neurons
spec:
spec:
devices:
requests:
- name: neurons
deviceClassName: neuron.aws.com
selectors:
- cel:
expression: device.attributes['neuron.aws.com'].instanceType == "trn2.48xlarge"
allocationMode: All
config:
- opaque:
driver: neuron.aws.com
parameters:
apiVersion: resource.neuron.aws.com/v1alphav1
kind: NeuronConfig
logicalNeuronCore: 1
requests: ["neurons"]
Beta Access#
Note
Neuron DRA driver is in private beta. Contact the Neuron product team to get access.
Once allow-listing is done, you will have access to the container image for the DRA driver, and the source code which will contain installation manifests and example workloads.
Prerequisites for the preview#
Kubernetes version - For preview, please use control plane 1.34 and 1.33 node AMI.
Instance type - Trn2.48xlarge
Installation#
Install the DRA driver using the script provided with the source code. Connect to your cluster from local box. The cluster should have at least one trn2.48xlarge node. Do not install the Neuron device plugin on the cluster! Check out the source code for the package and run:
Please confirm the cluster being used via:
kubectl config current-context
Then install the DRA driver:
./examples/scripts/install-dra-driver.sh <image uri>
Example 1 – Connected Neuron Devices#
This section will demonstrate how to run a workload that needs to request a subset of connected Neuron Devices from a trn2.48xlarge instance. Before DRA, this use case required using Neuron Scheduler Extension. With DRA, this allocation is enabled natively.
The supported subsets include set of 1, 4, 8 or 16. Specifically, these are resource.aws.com/devicegroup1_id, resource.aws.com/devicegroup4_id,
resource.aws.com/devicegroup8_id, resource.aws.com/devicegroup16_id respectively.
The sets of 4 and 8 are selected as shown in diagram below:
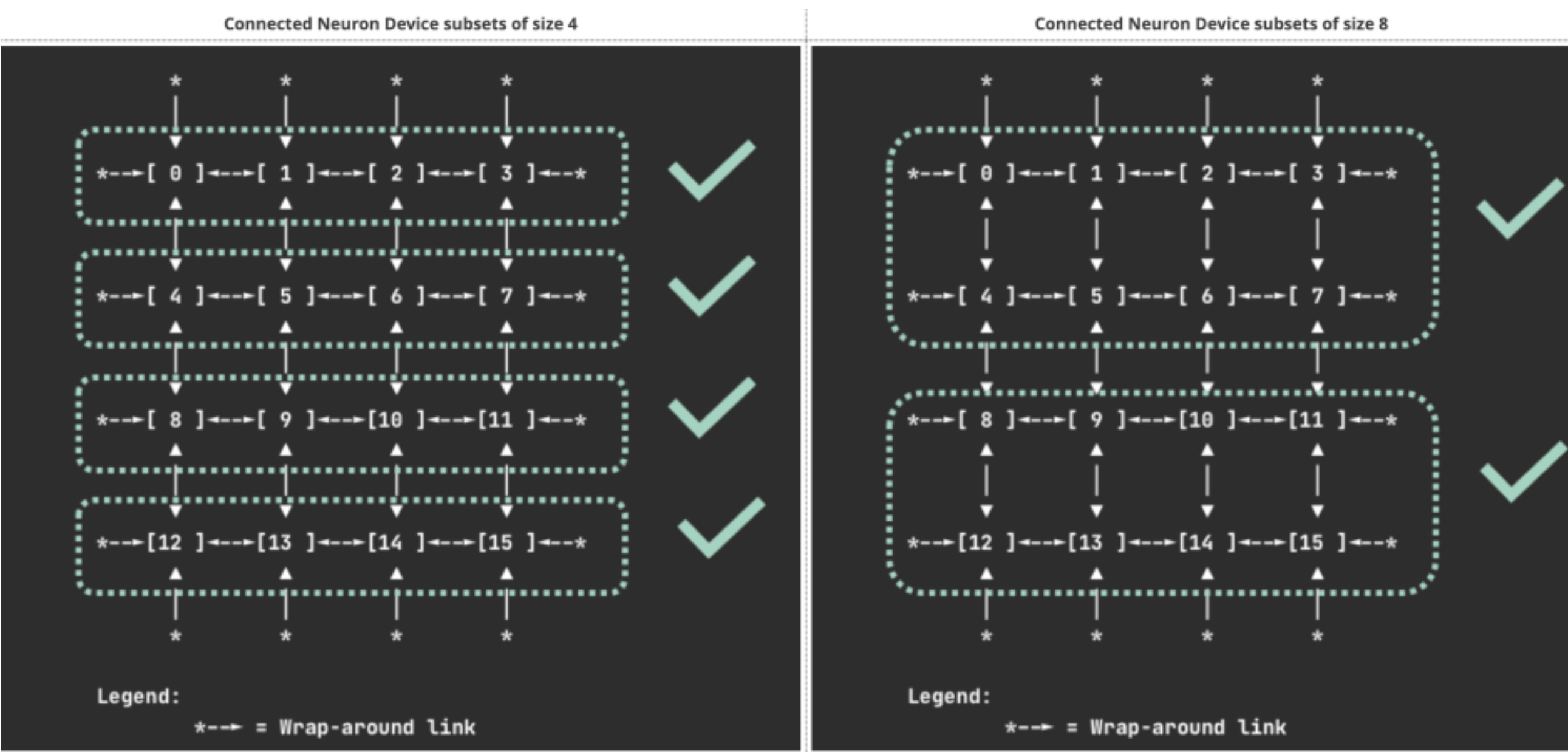
To enable a workload to consume a connected subset of Neuron Devices, first create a ResourceClaimTemplate that requests a connected set of
Neuron devices. From the package run:
kubectl apply -f examples/specs/1x4-connected-devices.yaml
This workload definition (which includes the ResourceClaimTemplate) is shown below for quick reference:
apiVersion: resource.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: ResourceClaimTemplate
metadata:
name: 1x4-connected-neurons
spec:
spec:
devices:
requests:
- name: neurons
deviceClassName: neuron.aws.com
allocationMode: ExactCount
count: 4
selectors:
- cel:
expression: "device.attributes['neuron.aws.com'].instanceType == 'trn2.48xlarge'"
constraints:
- requests: ["neurons"]
matchAttribute: "resource.aws.com/devicegroup4_id"
Next step is to reference the ResourceClaimTemplate in a pod definition as shown below:
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: pod0
labels:
app: pod
spec:
containers:
- name: ctr0
image: public.ecr.aws/ubuntu/ubuntu:22.04
command: ["bash", "-c"]
args: ["export; trap 'exit 0' TERM; sleep 9999 & wait"]
resources:
claims:
- name: neurons
resourceClaims:
- name: neurons
resourceClaimTemplateName: 1x4-connected-neurons
Deploy the above workload using kubectl apply. When the pod is running, examine the related ResourceClaim using:
kubectl get resourceclaim -o yaml
The resourceclaim output will show the 4 Neuron Devices that were allocated to the pod. An example is shown below. These will be connected Neuron
Devices.
[devbox]$ kubectl get pod
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
---------------------------------------
pod0 1/1 Running 0 3s
[devbox]$ kubectl get resourceclaim
NAME STATE AGE
---------------------------------------------
pod0-neurons-zdk76 allocated,reserved 9s
[devbox]$ kubectl get resourceclaim pod0-neurons-zdk76 -o yaml
Status shown below:
status:
allocation:
devices:
results:
- adminAccess: null
device: neurondevice2
driver: neuron.aws.com
pool: ip-1-1-1-1.region.compute.internal
request: neurons
- adminAccess: null
device: neurondevice3
driver: neuron.aws.com
pool: ip-1-1-1-1.region.compute.internal
request: neurons
- adminAccess: null
device: neurondevice1
driver: neuron.aws.com
pool: ip-1-1-1-1.region.compute.internal
request: neurons
- adminAccess: null
device: neurondevice0
driver: neuron.aws.com
pool: ip-1-1-1-1.region.compute.internal
request: neurons
Note
The RCT name can be simplified to communicate the intent of the allocation and abstract the allocation details away from ML developers.
Example RCT1 - “xl” - Allocate All 16 devices
apiVersion: resource.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: ResourceClaimTemplate
metadata:
name: xl-trn2
spec:
spec:
devices:
requests:
- allocationMode: ExactCount
count: 16
deviceClassName: neuron.aws.com
name: neurons
selectors:
- cel:
expression: device.attributes['neuron.aws.com'].instanceType == 'trn2.48xlarge'
Example RCT2 - large - Allocate 8 devices
apiVersion: resource.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: ResourceClaimTemplate
metadata:
name: l-trn2
spec:
spec:
devices:
constraints:
- matchAttribute: resource.aws.com/devicegroup8_id
requests:
- neurons
requests:
- allocationMode: ExactCount
count: 8
deviceClassName: neuron.aws.com
name: neurons
selectors:
- cel:
expression: device.attributes['neuron.aws.com'].instanceType == 'trn2.48xlarge'
Example RCT2 - 2.26-driver – Allocate 8 devices with driver version at the driver published by Neuron SDK 2.26
apiVersion: resource.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: ResourceClaimTemplate
metadata:
name: 2.26-driver-trn2
spec:
spec:
devices:
constraints:
- matchAttribute: resource.aws.com/devicegroup8_id
requests:
- neurons
requests:
- allocationMode: ExactCount
count: 8
deviceClassName: neuron.aws.com
name: neurons
selectors:
- cel:
expression: device.attributes['neuron.aws.com'].instanceType == 'trn2.48xlarge' &&
device.attributes['neuron.aws.com'].neuronDriverVersion == '2.24.7.0'
Attributes published by Neuron DRA driver are described in the source code at pkg/consts/neuron_attributes.go. The RCT can set up expressions that can filter devices based on the attributes.
Example 2 - Dynamic LNC config#
This example shows how to set LNC per workload. Earlier, overriding LNC on a Node required a node template. With DRA, workloads can
override default LNC via ResourceClaim.
Apply the following workload definition:
kubectl apply -f examples/specs/lnc-setting-trn2.yaml
This workload definition (which includes the ResourceClaimTemplate) is shown below for quick reference:
apiVersion: resource.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: ResourceClaimTemplate
metadata:
name: all-neurons-lnc-1
spec:
spec:
devices:
requests:
- name: neurons
deviceClassName: neuron.aws.com
selectors:
- cel:
expression: "device.attributes['neuron.aws.com'].instanceType == 'trn2.48xlarge'"
allocationMode: All
config:
- requests: ["neurons"]
opaque:
driver: neuron.aws.com
parameters:
apiVersion: neuron.aws.com/v1alphav1
kind: NeuronConfig
logicalNeuronCore: 1
Then deploy a pod that references the above ResourceClaimTemplate as shown below:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: pod0
labels:
app: pod
spec:
containers:
- name: ctr0
image: public.ecr.aws/ubuntu/ubuntu:22.04
command: ["bash", "-c"]
args: ["export; trap 'exit 0' TERM; sleep 9999 & wait"]
resources:
claims:
- name: neurons
resourceClaims:
- name: neurons
resourceClaimTemplateName: all-neurons-lnc-1
Example 3 – Four Node Inference on trn2u.48xlarge#
A trn2u.48xlarge Trn2 UltraServer has 4 Trn2 nodes interconnected by Neuron Links.
trn2u.48xlarge instances can be allocated in set of 1, 2, or 4. The Neuron DRA driver can utilize 1 or more ResourceClaimTemplate definitions to convey the
desired size of the set. The ResourceClaimTemplate allows end users to specify “UltraServerConfig” to declare their intent to use all 4 nodes of
the UltraServer. This configuration value is passed by the Neuron DRA driver to the Neuron runtime and collectives inside the container.
Example yaml for 4-node inference on trn2u.48xlarge:
apiVersion: resource.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: ResourceClaimTemplate
metadata:
name: us-4-node-config
spec:
spec:
devices:
requests:
- name: neurons
deviceClassName: neuron.aws.com
selectors:
- cel:
expression: "device.attributes['neuron.aws.com'].resourceType == 'neuron_node'"
allocationMode: ExactCount
count: 1
config:
- requests: ["neurons"]
opaque:
driver: neuron.aws.com
parameters:
apiVersion: neuron.aws.com/v1alphav1
kind: UltraServerConfig
ultraserverMode: 4
---
apiVersion: leaderworkerset.x-k8s.io/v1
kind: LeaderWorkerSet
metadata:
name: vllm
annotations:
leaderworkerset.sigs.k8s.io/exclusive-topology: neuron.amazonaws.com/ultraserver-server-id-4
spec:
rolloutStrategy:
type: RollingUpdate
rollingUpdateConfiguration:
maxUnavailable: 1
maxSurge: 1
# Two replica groups of 4 nodes each, i.e. two ultraservers
replicas: 2
leaderWorkerTemplate:
size: 4
restartPolicy: RecreateGroupOnPodRestart
leaderTemplate:
metadata:
labels:
role: leader
spec:
containers:
- name: vllm-leader
image: public.ecr.aws/ubuntu/ubuntu:22.04
command:
- sh
- -c
- "sleep infinity"
resources:
claims:
- name: one-node-from-ultraserver
resourceClaims:
- name: one-node-from-ultraserver
resourceClaimTemplateName: us-4-node-config
workerTemplate:
metadata:
labels:
role: worker
spec:
containers:
- name: vllm-worker
image: public.ecr.aws/ubuntu/ubuntu:22.04
command:
- sh
- -c
- "sleep infinity"
resources:
claims:
- name: one-node-from-ultraserver
resourceClaims:
- name: one-node-from-ultraserver
resourceClaimTemplateName: us-4-node-config
FAQs#
Can DRA plugin co-exist with other device plugins?#
Device plugins and the DRA plugin can coexist in the same cluster, but not for the same node. As of now, the two mechanisms act independently. Neuron is preparing an upcoming feature that will allow device plugin based allocations to work with DRA, but the feature is still in alpha and not enabled on EKS. Ref: Extended Resource.
Is DRA replacing Neuron Device Plugin and Scheduler Extension?#
We will continue to support the Neuron Device Plugin and Sthe cheduler Extension as long as:
Upstream Kubernetes continues to support device plugins.
EKS continues to support Kubernetes versions below 1.34 (which do not support DRA).
What Kubernetes versions are supported?#
Kubernetes control plane must be on 1.34. For Node AMI, we support 1.33 and 1.34.2. We do not support Node AMI for 1.34 or 1.34.1 since it had a regression in DRA. Upstream issue: Kubernetes Issue #133920
Where can I learn more about how to put together RCT using CEL expressions?#
To learn more about RCTs, please visit Kubernetes Dynamic Resource Allocation. To learn more about CEL expressions, please visit CEL Language. Send us feedback on the beta and let us know which additional RCT examples you would like us to provide in the source code.
This document is relevant for: Inf1, Inf2, Trn1, Trn2, Trn3
