This document is relevant for: Trn1, Trn2, Trn3
ZeRO-1 Tutorial#
What is ZeRO-1?#
ZeRO-1 (Zero Redundancy Optimizer Stage 1, https://arxiv.org/abs/1910.02054) is an optimization technique for large-scale deep learning models. It is a memory efficient variation of data parallelism. ZeRO leverages the aggregate computation and memory resources of data parallelism to reduce the memory and compute requirements of each accelerator used for model training. ZeRO reduces the memory consumption of each accelerator by partitioning the various model training states (weights, gradients, and optimizer states) across the available devices in the distributed training hardware. ZeRO is being implemented as incremental stages of optimizations. In stage 1, the optimizer states (e.g., for Adam optimizer, 32-bit weights, and the first, and second moment estimates) are partitioned across the processes, so that each process updates only its partition.
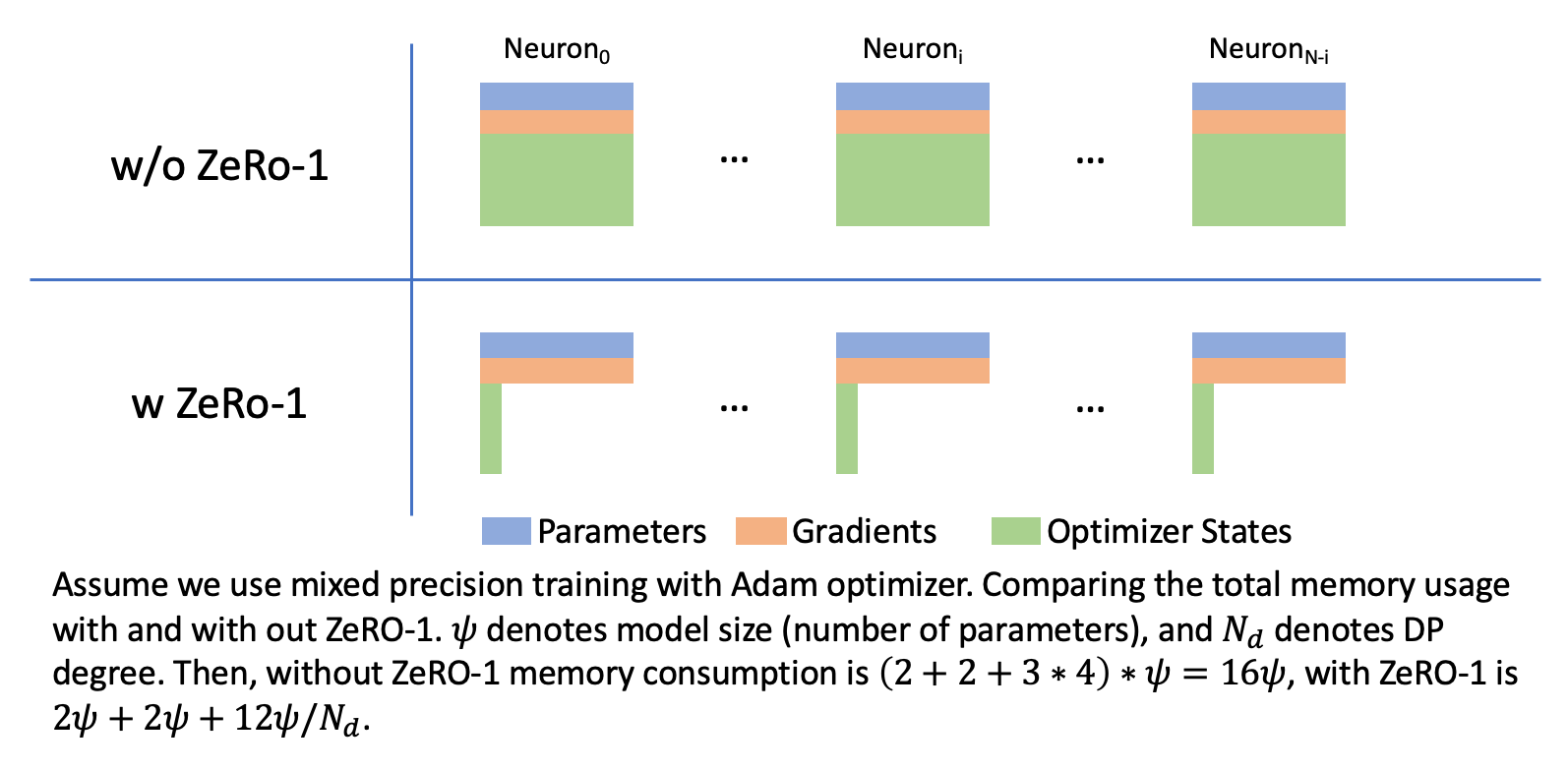
We implemented an XLA-friendly version of ZeRO-1 and it has been merged in open-source PyTorch/XLA project. Users can use it to enable ZeRO-1 algorithm by simply wrapping the origin optimizer as shown below.
# Before:
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.0001)
# After
optimizer = ZeroRedundancyOptimizer(model.parameters(), torch.optim.Adam, lr=0.0001)
Then just call optimizer.step() directly, the wrapped optimizer will
handle the distributed operations automatically.
The above code snippet illustrates the basic usage. Generally, users can
use ZeRO-1 optimizer like a normal optimizer. In addition,
ZeroRedundancyOptimizer also provides other features: enable
gradient clipping or use other data type for wrapped optimizer. Note
that though the most of optimizers can be used with ZeRO-1, optimizers
that compute norm for parameters (e.g. LAMB) might lead to accuracy
disparities compared to using original local optimizer when using
ZeRO-1, because these optimizers cannot get full parameters but shards.
Usage#
To enable ZeRO-1 optimizer, just import it and replace origin optimizer with ZeRO-1 wrapped version
from torch_xla.distributed.zero_redundancy_optimizer import ZeroRedundancyOptimizer
...
...
device = xm.xla_device()
model = model.to(device)
optimizer = ZeroRedundancyOptimizer(model.parameters(), AdamW, lr=0.001)
Then in training loop, just call optimizer.step() , note that we
should not use xm.reduce_gradients() or xm.optimizer_step() as
gradient reduction will be handle by ZeRO-1.
...
loss.backward()
xm.mark_step()
optimizer.step()
xm.mark_step()
ZeRO-1 optimizer also provides some additional features, user can pass these arguments to the wrapper constructor:
Change
optimizer_dtypeto choose data dtype used by optimizer, default istorch.float32. For example, when parameter data type is bfloat16, setoptimizer_dtypeto be float32 to enable ‘master weight’.Change
grad_clippingto enable grad clipping, default isTrue.Change
max_normto determine the maximum norm value used by grad clipping, default is1.0.Change
use_grad_acc_hookto enable using buffers to store gradients, it will use the same data type asoptimizer_dtypeto accumulate gradients. (Added in neuron 2.19.0 release).Change
higher_cc_precisionto force reduce-scatter operator to use the same data type asoptimizer_dtype, default isFalse. Whenuse_grad_acc_hookisTrue, it has no effects. (Added in neuron 2.19.0 release).
Note: ZeRO-1 optimizer now forces to use the same data type as parameters for all-gather operator. (Changed in neuron 2.19.0 release)
GPT2-XL Pretraining Tutorial#
Setup#
We use single Trn1.32xlarge instance. Follow Install PyTorch Neuron on Trn1 to setup the environment first. For all the commands below, make sure you are in the virtual environment that you have created above before you run the commands:
requirements.txt: We pin the following Hugging Face Library versions necessary for the tutorial
transformers==4.27.3
accelerate==0.17
tensorboard==2.12.2
source ~/aws_neuron_venv_pytorch/bin/activate
git clone https://github.com/aws-neuron/aws-neuron-samples.git
cd aws-neuron-samples/torch-neuronx/training/zero1_gpt2
python3 -m pip install -r requirements.txt
The specific files you need for this tutorial:
config_1p5B_gpt2.json: The model configuration used in the tutorial for GPT 2.7B Neo
neuron_utils.py: includes utility functions and the logging tools
run_clm_no_trainer.py: the main training script that runs the actual training
run_clm.sh: the shell script to launch the training job
Dataset#
For the dataset, we use the wikitext dataset, specifically
wikitext-103-raw-v1, provided by the HuggingFace
https://huggingface.co/datasets/wikitext. The data will be preprocessed
the first time running through the training script and then preprocessed
data will be cached in the HuggingFace cache directory for any future
training runs.
If the main process downloads the dataset, tokenizes the data and groups them together successfully, the expected output would be as below at the beginning of the training.
***** Running training *****
Num examples = 114248
Num Epochs = 29
Instantaneous batch size per device = 1
Total train batch size (w. parallel, distributed & accumulation) = 32
Gradient Accumulation steps = 1
Total optimization steps = 100000
Training#
The GPT2 python fine-tuning script is adapted from the example run_clm_no_trainer.py in huggingface/transformers. It incorporates the Accelerate huggingface/accelerate. Given its beta stage, some modifications are needed, along with the bridge code to XLA. Particularly, some workarounds to support Accelerate for the training script are listed in “Known Issues Workarounds and Limitations” below.
In this example, we use GPT2-xl as example, and show the training steps with mixed precision (bfloat16 and float32)
single node training:
# Run precompile and training
neuron_parallel_compile bash run_clm.sh MIXED wikitext-103-raw-v1
bash run_clm.sh MIXED wikitext-103-raw-v1
multi-node training, run:
sbatch run_clm_compile.slurm
then
sbatch run_clm.slurm
Known Issues, Work-arounds and Limitations#
Error message:
ValueError: invalid literal for int() with base 10: ''. Simply re-run the script can solve this issue. This issue is already solved in the newer versions of transformers, see huggingface/transformers#22427.Accelerator API workarounds:
Error message: “Gradient accumulation is not supported on TPU. Please set gradient_accumulation_steps to 1 and don’t pass in a GradientAccumulationPlugin object.” More context here: huggingface/accelerate#479. The training still works by commenting out the assertion and avoid using the accumulation wrapper with accelerator.accumulate(model)
Accelerator.prepare call: We have noticed that using the optimizer returned by this API are not directly reusable. It is due to gaps in configuring accelerate API for XLA devices.
This document is relevant for: Trn1, Trn2, Trn3
