This document is relevant for: Trn1
Amazon EC2 Trn1/Trn1n Architecture#
On this page, we provide an architectural overview of the AWS Trn1/Trn1n instances, and the corresponding Trainium NeuronChips that power them (Trainium chips from here on).
Trn1/Trn1n Architecture#
An EC2 Trn1/Trn1n instance is powered by up to 16 Trainium chips.
The Trn1.2xlarge instance size allows customers to train their models on a single Trainium chip, which is useful for small model training, as well as for model experimentation. The Trn1.32xlarge and Trn1n.32xlarge instance size come with a high-bandwidth and low-latency NeuronLink-v2 chip-to-chip interconnect, which utilizes a 2D Torus topology. This is useful for collective communication between the Trainium chips during scale-out training, as well as for pooling the memory capacity of all Trainium chips, making it directly addressable from each of the chips.
In a Trn1/Trn1n server, the Trainium chips are connected in a 2D Torus topology, as depicted below:
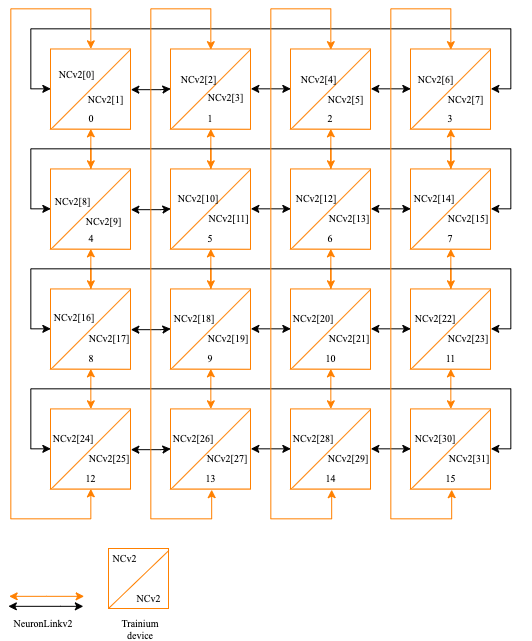
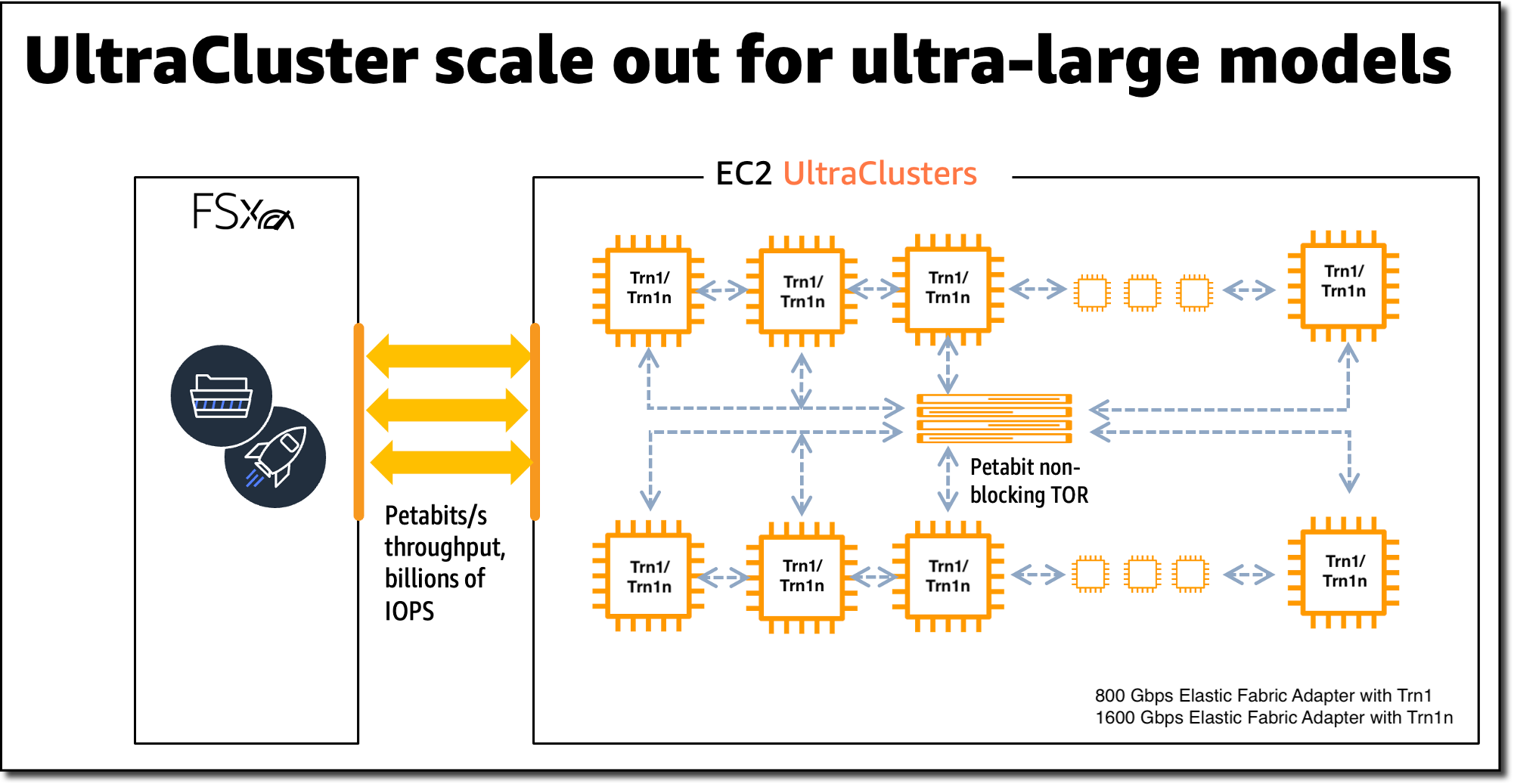
The Trn1/Trn1n instances are also available in an EC2 UltraCluster, which enables customers to scale Trn1/Trn1n instances to over 100,000 Trainium chips, and leverage the AWS-designed non-blocking petabit-scale EFA networking infrastructure.
This document is relevant for: Trn1
