Neuron Collective Communication#
Introduction#
Collective Communications is an integral component of distributed ML training. Multiple training nodes exchange information during ML training via Collective Communication operators such as all-reduce. Neuron provides hardware support for the execution of Collective Communication with the Neuron SDK responsible for the hardware configuration and for the execution orchestration. Neuron provides the following Collective Communication operators:
all-reduce
all-gather
reduce-scatter
Neuron also provides the following peer to peer operators:
send
receive
Support for additional Collective Communication operators might be added in future releases. Neuron devices are connected via NeuronLinks within a single instance and EFA links between instances. All NeuronLinks transfer the data directly between Neuron device and between Neuron devices and EFA devices bypassing the host to achieve high bandwidth and low latency.
Collective Communication support on Neuron requires installation of 3 separate packages:
aws-neuronx-runtime-lib- supports execution on Neuron, not specific to Collective Communication and is always requiredaws-neuronx-collectives- supports Collective Communication execution on a single instance and on multiple instances.efa_installer- low level libraries and drivers to support Collective Communication execution over EFA, required to support Collective Communication on multiple instances.
ML models need to be compiled by the Neuron compiler before they can be executed on Neuron devices. The result of the compilation is a binary object containing computational instruction and data movement instructions. Any Collective Communication operators encountered during compilation are converted to the place holder instructions to be filled by the runtime/collectives libraries during load and execution. This approach allows Neuron compiler to be unaware of the specific physical topology connecting Neuron devices. Once a compiled mode is placed on Neuron devices the runtime/collectives libraries generate the appropriate data movement instructions based on the placement. For example, a different set of instructions is generated when the next rank is connected via NeuronLinks or via EFA. Neuron executes Collective Communication operators using dedicated hardware that is not shared with computational resources. That allows Neuron to execute compute and communication in parallel. For example Neuron can all-reduce gradients of one layer while the gradients for another layer are computed. Overlapping compute and communication can result is lower latency and higher performance.
For more details, see Compute-Communications Overlap.
trn1.32xlarge topology#
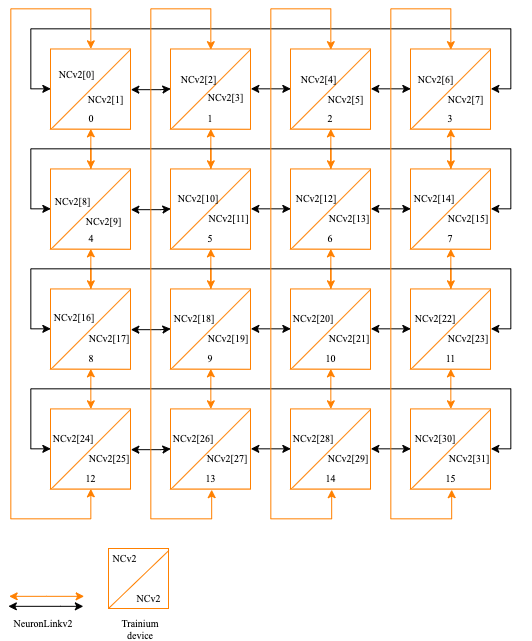
Trn1.32xl 2D torus topology
On a single trn1.32xlarge instance Neuron devices are connected in a 2D torus topology supporting Collective Communication operators in sets of 2, 8 and 32 ranks. Other set sizes might be supported in future releases. A single instance topology can be further extended across multiple instances using EFA NeuronLinks.
For example an 8x4 topology on a single instance, such as 8 rank tensor parallel and 4 ranks data parallel can be extended across multiple instances creating a large tensor/data parallel training cluster.
trn1.2xlarge topology#
Trn1.2xlarge instance type contains a single Neuron device with two NeuronCores. This instance type supports only 2 ranks Collective Communication operators. EFA is not available on trn1.2xlarge and the ranks cannot be extended beyond a single instance.
inf2.48xlarge topology#
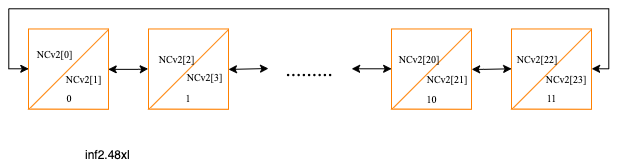
inf2.48xlarge topology
On inf2.48xlarge instance Neuron devices are connected in a ring via NeuronLink. Any even number of ranks for Collective Communication operators is supported provided that the ranks occupy consecutive Neuron devices. However, when using any number of ranks other than 24 (full instance) full performance of the ring is not utilized.
Inf2 other instance sizes topologies#

inf2 other instance sizes topologies
On other inf2 instance sizes Neuron devices are connected bi-directionally. Any even number of ranks for Collective Communication operators is supported provided that the ranks occupy consecutive Neuron devices. Collective Communication performance is similar to the performance on inf2.48xlarge when fewer than 24 ranks are used.
