This document is relevant for: Inf2, Trn1, Trn2, Trn3
Neuron Persistent Cache#
PyTorch Neuron (torch-neuronx) uses torch-xla, and torch-xla operates in lazy mode. In other words, every operation in training script
is recorded in a graph. The graph is executed only when the results are requested by
the user when they use print or xm.mark_step. Requesting results tells
torch-xla that the recorded graph needs to be executed.
Before executing the graph on a Neuron device, torch-xla would call Neuron Compiler (neuronx-cc) to compile the graph into Neuron specific
graph. Then the graph is executed on the NeuronCore/s. Compiling the graph involves
running optimizations that can make use of the NeuronCore/s efficiently. Running these
optimizations can be expensive and can result in long compile times. To save the
users from compiling these graphs at every iteration, torch-xla maintains an
in-memory cache called Just in Time (JIT) cache. When the user re-runs the same graph (eg. 2nd
iteration of the training run), torch-xla would check in this JIT cache and re-use
the cached compilation result, thereby avoiding the wait times.
Since the JIT cache is an in-memory cache, it needs to be constructed every time the training script is
run. Hence, if the user re-runs the training script, a new JIT cache is created. This causes a compilation for the first training graph.
To avoid such compilations across training runs, PyTorch Neuron (torch-neuronx) has built an on-disk
Neuron Persistent Cache. Since this cache is on-disk, its persistent across training runs. So
now, when a graph is compiled for the fist time, the compilation result is saved in
Neuron Persistent Cache. When the user re-runs the training script, since the JIT cache is not
ready, it would send the graph for compilation. PyTorch Neuron (torch-neuronx) would then check if
the compiled result is present in the Neuron Persistent Cache, if yes, it would return with the
compiled result. This on-disk cache thereby avoids compilations across training runs.
This cache is enabled by default for Neuron’s PyTorch/XLA flow (training) as well as
transformers-neuronx LLM inference package.
The default cache path is the directory /var/tmp/neuron-compile-cache.
Look at the diagram below on the end to end flow:
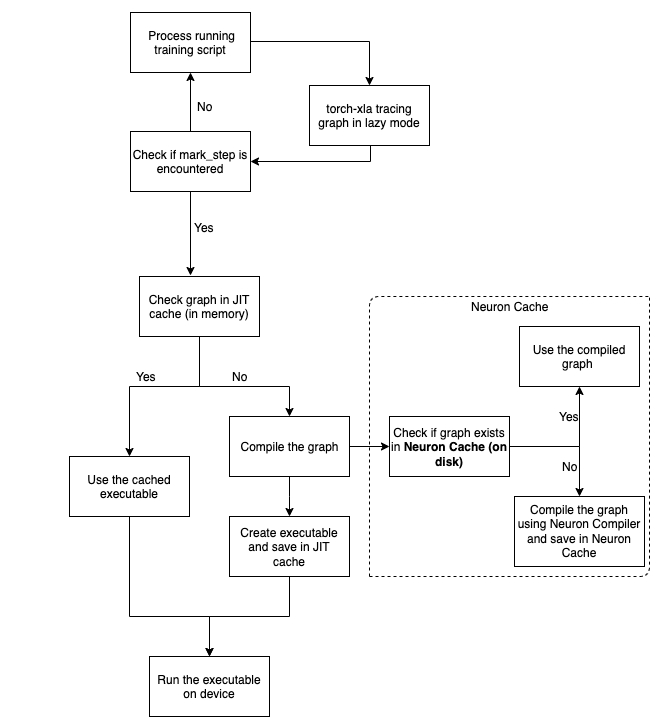
As seen from the diagram, the operations are recorded in a graph in lazy mode and only
when a mark_step is hit, the graph is executed. Before execution, the graph passes through
two caches to check if we have compiled the graph sometime in the past. If yes, we reuse
the compilation result and execute with it. This avoid duplicate compilations.
One thing to note, both JIT cache and Neuron Cache are complementary to each other.
JIT cache prevents duplicate compilation within a run and Neuron Cache prevents duplicate
compilations across training runs. For example, within a training script, we have a training
loop that iterates through the dataset. The first iteration would trace a unique graph
and the following iteration would trace a graph that is similar to the first one. In this case,
the subsequent iterations would hit the JIT cache and reuse the result. However, to save
users from compiling for the first iteration graph, Neuron Persistent Cache would be used. In this case,
the very first time when the script is run, the Neuron Persistent Cache would be updated. Going forward
when we re-run the training script, compilation results from Neuron Persistent Cache would be used.
To better understand how Neuron Persistent Cache works, consider the example below:
import torch
import torch_xla
import torch_xla.core.xla_model as xm
device = xm.xla_device()
t1 = torch.randn(3, 3).to(device)
t2 = t1 / 0.5
x = t2.cpu()
Running the above example produces the following logs:
2023-08-25 21:51:36.000433: INFO ||NCC_WRAPPER||: Compile cache path: /var/tmp/neuron-compile-cache
.
Compiler status PASS
Re-running the above script would fetch the graph from the neuron cache and you would see logs as follows:
2023-08-25 21:52:23.000451: INFO ||NCC_WRAPPER||: Compile cache path: /var/tmp/neuron-compile-cache
2023-08-25 21:52:23.000453: INFO ||NCC_WRAPPER||: Using a cached neff at /var/tmp/neuron-compile-cache/neuronxcc-2.8.0.25+a3ad0f342/MODULE_198775565831884870+d41d8cd9/model.neff. Exiting with a successfully compiled graph.
As you can see, the next run picks the compiled graph from cache, thereby saving the compilation time. The cache uses hash of the Neuron compiler flags and XLA graph as the key. If the Neuron compiler version or XLA graph changes, you will see recompilation. Examples of changes that would cause XLA graph change include:
Model type and size
Batch size
Optimizer and optimizer hyperparameters
Location of xm.mark_step()
To keep cache size small and to enable weights/parameters updates without recompilation, only the compute graphs are cached when using transformers-neuronx (weights/parameters are inputs to the compute graphs) and training flow using torch-neuronx’s XLA (weights/parameters are inputs and outputs of the compute graphs). Note that this caching mechanism doesn’t apply to the torch-neuronx trace API where the weights/parameters are frozen and converted to constants, then compiled together with the compute operations (traced graphs with frozen weights/parameters are not cached).
All compilation results are saved in the cache. To disable the cache, you
can pass --no_cache option via NEURON_CC_FLAGS:
os.environ['NEURON_CC_FLAGS'] = os.environ.get('NEURON_CC_FLAGS', '') + ' --no_cache'
The default cache path is the directory /var/tmp/neuron-compile-cache.
To change the cache’s location, pass cache_dir=<cache_url>
option via NEURON_CC_FLAGS or NEURON_COMPILE_CACHE_URL=<cache_url> environment variables:
os.environ['NEURON_CC_FLAGS'] = os.environ.get('NEURON_CC_FLAGS', '') + ' --cache_dir=<cache URL>'
os.environ['NEURON_COMPILE_CACHE_URL'] = '<cache_URL>'
The cache URL specified using --cache_dir is prioritized over that specified using NEURON_COMPILE_CACHE_URL if both are set.
If <cache_url> starts with s3://, it will use the AWS S3 URL as the cache location, provided that the corresponding S3 bucket exists and is both readable and writeable.
You can change the verbose level of the compiler by adding log_level to either WARNING, INFO
or ERROR. This can be done as follows:
os.environ['NEURON_CC_FLAGS'] = os.environ.get('NEURON_CC_FLAGS', '') + ' --log_level=INFO'
A graph compilation can fail because of a compilation error or an environment issue (for example, compilation is interrupted by ctrl-C). The graph would be marked as failed and subsequent rerun would encounter message like below:
INFO ||NCC_WRAPPER||: Got a cached failed neff at /var/tmp/neuron-compile-cache/neuronxcc-2.8.0.25+a3ad0f342/MODULE_12486829708343293975+d41d8cd9/model.neff. Will skip compilation, please set --retry_failed_compilation for recompilation.
To retry compilation,
add --retry_failed_compilation in NEURON_CC_FLAGS environment variable. When the script is reran, all the previously failed compilations are recompiled and fresh results are saved in the cache.
os.environ['NEURON_CC_FLAGS'] = os.environ.get('NEURON_CC_FLAGS', '') + ' --retry_failed_compilation'
Note that all flags demonstrated above will be parsed by a tool called neuron_cc_wrapper, which is a wrapper over Neuron Compiler CLI to provide caching mechanism. All these flags will not be passed into Neuron Compiler CLI.
This document is relevant for: Inf2, Trn1, Trn2, Trn3
